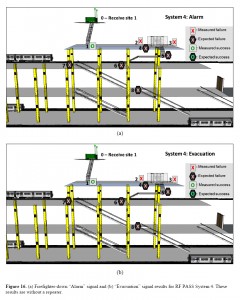
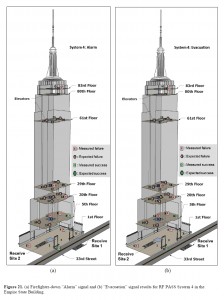
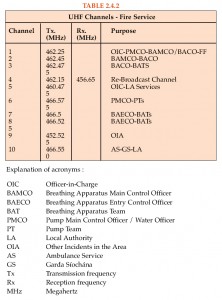
2013-06-09: Further to yesterday’s post … and my use of the phrase ‘Adapted to Local Context and Heritage (fr: le Patrimoine)’ … in relation to Sustainable Fire Engineering Design Solutions … or, indeed, Sustainable Design Solutions generally …
The International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) … has just published the hard-copy version of … ‘Le Patrimoine, Moteur de Développement : Enjeux et Projets‘ … the proceedings from the 2011 ICOMOS International Scientific Symposium, which was held in conjunction with the 17th ICOMOS General Assembly in early December 2011 … and organized by ICOMOS-France (www.icomosfrance.fr).
This bilingual (French and English) document provides a summary of the 4 Main Issues discussed during the Paris Symposium.
Manifested here … is a profound re-imagining of the concept of ‘heritage’, and its symbiotic relationship with ‘local context’ … which also now facilitates a synergetic fusion of ‘heritage’ with mainstream sustainable development theory and implementation. I have highlighted key passages …
.
HERITAGE – DRIVER OF DEVELOPMENT
The Theme of the International Scientific Symposium, which forms part of the ICOMOS General Assembly, is the role of heritage in the creation of tomorrow’s society.
The effects of globalization, which are manifested in growing trends towards standardization and westernization, bring various forms of instability to human societies. Until now, heritage has been confined to the role of passive conservation of the past, and so has often been seen as a burden hindering development. In the future, it should be called upon instead to play a major role, re-establishing cultural identity and diversity as key reference points for development; these factors are currently endangered, yet vital. There is therefore a need to reassess the role of heritage in a constructive way.
The concept of heritage, which ranges from designated historic monuments to a jumble of memories, first needs a clear definition which identifies its inherent nature and sets out its boundaries and limits, now and in the future.
As it would be impossible to cover all these issues at the Symposium, it is proposed to focus on the following four issues, chosen for their fundamental importance or contemporary relevance …

1. Regional Development
As more and more people abandon small towns and the countryside, migrating to large conurbations, urban development has become anarchic, ad-hoc and difficult to control. This has already had serious, even catastrophic, results … in particular:
– The disruption of spatial scale and the loss of landmarks ;
– The breakdown of social relationships, loss of communal solidarity, concerns over security, extremist and violent demonstrations ;
– An imbalance between the city – where most concerns now focus and where most development projects take place – and the countryside, where the issue is no longer merely rural decline, but rather the complete socio-economic and cultural collapse of forgotten populations ;
– The squandering and trivialization of space, which is a non-renewable resource, and in particular the loss of landscapes and farmland, resulting from both extensive urban encroachment and land being left to lie fallow.
It is vital to return to a more balanced form of development. This will be achieved by replacing the principle of urban expansion with that of regional development, which takes into account both the countryside and secondary urban centres (small and medium-sized towns), as part of a balanced network. In this context, lessons from our heritage will again be valued as an inspiration for new developments: time-honoured frameworks, traditional plot sizes, methods of organization (urban historic core zones), communication (by land – rail – water), and energy generation (small-scale solar and hydroelectric power stations), etc.

2. Sustainable (Human & Social) Development – Return to the Art of Building !
The second half of the 20th Century was marked by the frantic exploitation of fossil fuels and is credited with the international spread of Western lifestyles and buildings, said to represent ‘progress’ but nevertheless creating a decisive break with traditional models. The goals we have today for energy saving and recycling require a fundamental change in the character of both new and old buildings, in line with the following three points:
– Expertise in Re-Use. Until the 1950’s, heritage buildings – especially vernacular ones – provided countless examples of successful adaptation to the physical environment (location, orientation, protection from sun, wind, and climate); use of local materials (earth – wood – stone, etc.); traditional techniques providing / guaranteeing the greatest opportunities to acquire and perfect artisanal skills; and an optimum capacity for recycling. The resulting buildings address today’s requirements for sustainable development particularly well. Where historic buildings are capable of residential re-use according to modern sustainability criteria, we must be able to measure and maximise their current performance before adapting them according to new artificial design standards.
– Expertise in Building. In terms of new construction, recent examples have shown the ability of traditional practices to create architecture that is indisputably creative and modern/contemporary, and offer an alternative to artificial solutions proposed in response to new standards.
– Adapting to Sustainable Living. Rather than putting the entire onus on the built heritage, we must question our expectations about comfort and utilization. We need to abandon attempts to use sites for activities for which they are fundamentally not suited; modify usage according to the seasons (closing down places that are difficult to heat in winter); and, finally, reconsider our demands in terms of comfort, which have grown excessively and unreasonably over the last decades. The progress that would be made in the fields of environmental and public health is well known.

3. Development and Tourism
Heritage is a major part of the tourist industry, but at the same time, because of the mass consumption to which it is increasingly subject, it runs the risk of becoming meaningless, by fluctuating between preservation of museum pieces and theme-park caricatures. Cut off from its context, the real significance of heritage is drowned out by a feeble reflection, and its very nature is altered by excessive numbers of visitors and the facilities installed for them.
Several courses of action are available, among others:
– Rendering identification with cultural heritage tangible … by revealing and interpreting heritage in all the richness of its context and distinctiveness, and by encouraging public awareness of history through education and the wider media.
– Controlling public access … so as both to limit physical erosion and to ensure the comfort of visitors and provide the best conditions for them to understand and appreciate the value of heritage. Some preliminary reports on trials successfully undertaken at a number of buildings and Grands Sites [designated French cultural landscapes] may help in developing guidelines.

4. Economics of Development
“The Amphitheatre at Nîmes and the Pont du Gard have brought more to France than they ever cost the Romans.” This quotation from Abbé Grégoire in the second year of the French Republic remains valid today. Investment in our heritage produces particularly attractive returns. The cultural sector fully understands this, but adopts methods that tend to be rather commercial.
This investment must be better directed, by identifying targets and striving more for qualitative results rather than short-term profits.
.
.
END