2009-03-17: Pull closer to the screen … we can lower the sound level, and be honest with ourselves for a few minutes …
We have enabling legislation spewing out of our ears in the European Union on the subject of ‘fire safety, protection and evacuation for all’ … there is absolutely no shortage whatsoever !
The problem is that far too many fire officers (prevention and operations) and building control officers in local authorities, architects, engineers and quantity surveyors do not know and/or do not care about this issue.
Rates of compliance with legislation are very low. Proper compliance is such a rare thing … that you would almost feel like holding a party, in celebration, right there on the spot when it’s discovered ! This applies not only to Ireland and Great Britain … but to the rest of Europe as well.
And while many countries have already signed and ratified the 2006 United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which became an International Legal Instrument on 3rd May 2008 … and many more will do likewise during the course of the next year or two, including the United States of America (according to the Whitehouse WebSite !) … I am sure that few individuals in those countries have any understanding of Article 11 (text quoted in an earlier post).
Accessible Fire Engineering:
On that fateful morning of 11th September, 2001 … at the World Trade Center Complex in Lower Manhattan, New York City … we witnessed a catastrophic failure in common practices and procedures … at all levels …
– Architectural / Conventional (‘Ambient’) Engineering / Fire Engineering ;
– Building Management ;
– Emergency Responders / Firefighters / Rescue Teams ;
– Control Organizations Having Authority (AHJ’s) or Jurisdiction ;
– Fire Safety Objectives in Building Legislation, Codes & Standards.
This was a ‘real’ fire incident. It has been very, very closely examined in the intervening years. Disability was a major issue at the heart of the tragedy … 6% of WTC building occupants were people with mobility impairments … approximately 8%, in total, were people with disabilities. The overall number of People with Activity Limitations (2001 WHO ICF), however, was higher.
It is for this reason that three vital WTC Components have neatly dovetailed and fused … to realize an essential rational and empirical basis for a transformed fire engineering approach which can deal effectively with ‘fire safety, protection and evacuation for all’ of the people who use buildings … Accessible Fire Engineering … a subset of Sustainable Fire Engineering …
1. 2005 NIST(USA) NCSTAR 1 Final Report on 9-11 WTC 1 & 2 Tower Collapses.
2. 2008 NIST NCSTAR 1A Final Report on 9-11 WTC 7 Collapse.
3. Ongoing NYC-ATSDR World Trade Center Health Registry (established 2002).
Further Information about ‘fire safety, protection and evacuation for all’, the NIST 9-11 Reports and the WTC Health Registry … is available at the FireOx International WebSite …
Picking up, therefore, where I left off a few days ago …
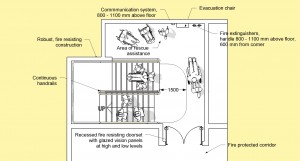
An ‘Area of Rescue Assistance’ in a Building should:
– adjoin every fire evacuation staircase in a building ;
– be located on every floor (note: fire evacuation routes at ground level should lead directly to the exterior) ;
– include adequate space for the people in wheelchairs, and their assistants, people using crutches, people with visual impairments, etc., who may be expected to use the area of rescue assistance during a fire emergency ;
– have good lighting at all times (note: lighting activation/de-activation by motion detection, for reasons of energy efficiency, should not be used in an area of rescue assistance) ;
– be clearly indicated with good signage ;
– be fitted with an accessible and reliable communication system placed at a height of 900 – 1 200 mm above finished floor level, facilitating direct contact with a person in the main fire and security control centre for the building ;
– be of sufficient size for the storage of a sufficient number of (powered) evacuation chairs, portable fire extinguishers, a fire hose reel and a manual fire alarm call point, a fire evacuation supply kit containing, for example, smoke hoods, suitable gloves to protect a person’s hands from debris when pushing his/her manual wheelchair, patch kits to repair flat tyres, and extra batteries for powered wheelchairs, etc.
The Size of an Area of Rescue Assistance should:
– relate to expected local usage during a fire emergency. When the number of people using/occupying/working in/visiting a specific building is considered … calculate how many may have to wait there, if the lifts/elevators cannot be used for evacuation and/or fire safety management procedures fail.
For example, if there are only two fire evacuation staircases on a floor in a building (on opposite sides of the building, of course), each area of rescue assistance should be designed to cater for the expected needs of the full floor.
Please also see the end of my Post: ‘U.S. Disability Statistics – EU Practical Application ?’, dated 2009-02-25.
Evacuation Chairs should be capable of:
– being safely and easily handled ;
– carrying people of large weight (up to 150 kg) ;
– going down staircases, which may be narrow and of unusual shape, particularly in existing buildings ;
– travelling long distances horizontally and externally, perhaps over rough ground, in order to reach a ‘place of safety’.
When it is necessary to go up an evacuation staircase to reach ground level … for example, from a basement or underground shopping centre … Powered Fire Evacuation Chairs should always be provided.
A ‘Reliable’ Buddy System:
In buildings with a reasonably stable user profile, e.g. workplaces, a Buddy System should be introduced throughout the building user population. For reliability and flexibility, e.g. to accommodate absence or holiday leave, a buddy system should always comprise at least 3 or 4 people.
In the case of a person using a wheelchair, his/her Buddy Unit should never be less than 4 people …

Fire Safety Management Procedures:
Prior to putting any Management Procedures into operation … and certainly before carving any of these procedures in stone … meaningful consultation should take place with building users and local fire authorities … which, particularly in the case of people with activity limitations, will produce the desired outcome of informed consent.
Informed Consent …
Consent freely obtained – without threats or improper inducements – after appropriate disclosure to a person of relevant, adequate and easily assimilated information in a form (e.g. oral, written, braille) and language understood by that person.
Personal Representative …
A person charged, under European Union or EU Member State national law, with the duty of representing another person’s interests in any specified respect, or of exercising specified rights on that person’s behalf – and including the parent or legal guardian of a child, i.e. a person under the age of 18 years, unless otherwise provided for by European Union or EU Member State national law.
Without wishing to be obscure, or to avoid the issue … Fire Safety Management Procedures need to be developed to suit each specific building, with its own building user population.
.
.
END