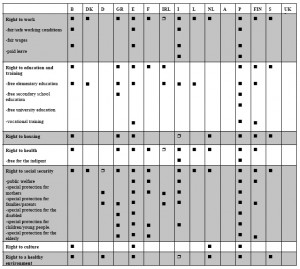
A few weeks ago … in a post dated 20 October 2010 … Japan in April & May 2010 – Accessibility-for-All ! … I discussed some of the many aspects which, together, facilitate a high level of quality in ‘real’, or actually realized, Built Environment Accessibility Performance in Japan … and I illustrated that quality with a number of photographs.
In time, I will add more photographs from my valuable ‘Accessibility in Japan’ Collection !
Note: Built Environment … Anywhere there is, or has been, a man-made or wrought (worked) intervention by humans in the natural environment, e.g. cities, towns, villages, rural settlements, roads, bridges, tunnels, transport systems, service utilities, and cultivated lands, lakes, rivers, coasts, seas, etc. … including the Virtual Environment.
Note: Social Environment … The complex network of real and virtual human interaction – at a communal or larger group level – which operates for reasons of tradition, culture, business, pleasure, information exchange, institutional organization, legal procedure, governance, human betterment, social progress and spiritual enlightenment, etc.
Note: Virtual Environment … A designed environment, electronically-generated from within the Built Environment, which may have the appearance, form, functionality and impact – to the person perceiving and actually experiencing it – of a real, imagined and/or utopian world.
However … many of these aspects are missing in European Approaches to Accessibility-for-All … and, typically, the level of Accessibility Performance which we are used to experiencing, and accepting, is inadequate, sloppy, poor … and to be direct and honest … BRUTAL !!
.
As far back as 2001 … in an Introduction to a Page on our Corporate WebSite illustrating the Inaccessibility of European Union Institutional Buildings … specifically, the European Parliaments in Brussels and Strasbourg … I wrote …
‘ Many times each year, our work takes us to Brussels, Luxembourg and Strasbourg.
In spite of all the rhetoric from European politicians, and the extensive body of European legislation actually in force at national and regional levels in every Member State … the inaccessibility of Institutional Buildings is shockingly and unacceptably bad … in some cases, dangerously so !
Yet, these buildings should represent, in built form, the ideals, values and aspirations of the peoples of Europe – as expressed in the EU Treaties.
What a bitter disappointment ! ‘
.
Today … France, in particular, continues to be a depressing experience … where Talk is far, far too cheap … and Good Accessibility Performance is still all too rare !!
Last Thursday, 25 November 2010 … I attended a Paris Meeting of the Editorial Team for the CIB W108 Report: ‘Sustainable Climate Change Adaptation in the Built Environment’. My airline flights from Dublin brought me in and out through Terminal 1 of Roissy Charles de Gaulle (CDG) Airport in Paris.
A spanking new automatically operated Métro (shuttle) … CDGVAL … connects Terminals 1, 2 & 3, various Multi-Storey Car Parks and Train Stations within the Airport Complex …
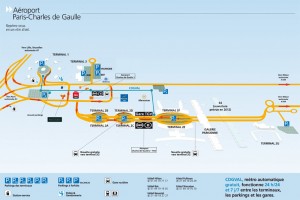
.

.
IF … you search hard enough on the CDG Airport WebSite, you will find these three highlighted short sentences under content with the title ‘Personne à Mobilité Réduite’ … total rubbish and complete bullshit when you actually see the airport’s buildings and many facilities. And … as usual, in French, the disability-related terminology is evil … and sucks !
‘Aéroports de Paris assure l’assistance des passagers handicapés et à mobilité réduite dés leur arrivée, et tout au long de leur parcours dans le terminal.
Aéroports de Paris a depuis longtemps entamé une démarche d’équipement et d’adaptation de ses terminaux pour faciliter les déplacements de tous.
Aujourd’hui, les problématiques d’accessibilités sont systématiquement prises en compte dans l’aménagement de nos infrastructures.’

.
Why is this relevant for us now … here in Ireland ?
The new scheme of Disability Access Certification, closely modelled on the existing highly problematic scheme of Fire Safety Certification … is undergoing a normal, introductory ‘teething’ process within this jurisdiction … and many questions about interpretation of the law and its operation are being asked.
Important Clarification: The Guidance Text contained in Technical Guidance Document M … is not Law … is not Prescriptive Regulation … is not ‘Deemed to Satisfy’ … and … because the guidance is so incomplete, incoherent and inadequate … does not even indicate Minimum Accessibility Performance !
Part M Functional Requirements – Access for People with Disabilities Second Schedule of the 1997 Building Regulations – As Amended by the Building Regulations (Amendment) Regulations, 2000 – Statutory Instrument No.179 of 2000
Access and Use M1 Adequate provision shall be made to enable people with disabilities to safely and independently access and use a building.
Sanitary Conveniences M2 If sanitary conveniences are provided in a building, adequate provision shall be made for people with disabilities.
Audience or Spectator Facilities M3 If a building contains fixed seating for audience or spectators, adequate provision shall be made for people with disabilities.
Definition for This Part M4 In this Part, ‘people with disabilities’ means people who have an impairment of hearing or sight or an impairment which limits their ability to walk, or which restricts them to a wheelchair.
Application of This Part M5 Part M does not apply to works in connection with extensions to and the material alterations of existing dwellings, provided that such works do not create a new dwelling.
.
Today in Ireland … Talk IS too cheap … and Good Accessibility Performance IS almost non-existent !!! Yes … and that even includes the work of those mighty superheroes in the Office of Public Works (OPW).
Furthermore … the big fun will really start when the New Part M Requirements come into operation on 1 January 2012 … and we will enter a surreal Alice’s Wonderland of Accessibility Ambiguity …
Part M Functional Requirements – Access and Use Second Schedule of the 1997 Building Regulations – As Amended by the Building Regulations (Part M Amendment) Regulations, 2010 – Statutory Instrument No.513 of 2010
Access and Use M1 Adequate provision shall be made for people to access and use a building, its facilities and its environs.
Application of The Part M2 Adequate provision shall be made for people to approach and access an extension to a building.
M3 If sanitary facilities are provided in a building that is to be extended, adequate sanitary facilities shall be provided for people within the extension.
M4 Part M does not apply to works in connection with extensions to and material alterations of existing dwellings, provided that such works do not create anew dwelling.
.
.
END