2010-11-02: For a long, long time … too long … I have been bleating on about the major and substantial difference between Sustainable Design and Green Design … or ‘Sustainability’ and ‘Green-ness’. See my previous Posts.
This bores me no end !
HOWEVER … there are some serious implications if this difference is not properly understood … particularly by individuals, groups or organizations attempting to advance the Application of Criteria which address Social and/or Ethical Concerns within, for example, the European Union’s Public Procurement Framework … or the EU’s Construction Product Framework.
The following is a nice little example of exactly what I am talking about … explained by no less an authority than the Directorate General for Environment in the European Commission itself … on its very own Public Procurement WebPage at http://ec.europa.eu/environment/gpp/index_en.htm … as viewed, by me, on 2010-09-12 …
[ For a moment, let’s just overlook the simplistic and crude ‘three pillars’ understanding of Sustainable Development. See my previous Posts.]
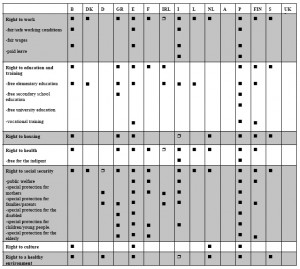
Sustainable Public Procurement (SPP) … means that public authorities seek to achieve the appropriate balance between the three pillars of sustainable development – economic, social and environmental – when procuring goods, services or works at all stages of the project.
Green Public Procurement (GPP) … means that public authorities seek to procure goods, services and works with a reduced environmental impact throughout their life cycle compared to goods, services and works with the same primary function that would otherwise be procured.
Practical Differences Between SPP & GPP !
GPP is often more easily accommodated than SPP within the existing legal and practical framework of procurement. Green requirements can be included in technical or performance-based specifications for products, services and works. Provided the conditions set out in the ‘Helsinki Bus’ and ‘Wienstrom’ Cases, and Evropaïki Dynamiki vs. European Environment Agency (EEA) … are met, green award criteria can also be applied (further information on these cases is available at http://ec.europa.eu/environment/gpp/case_law_en.htm).
The application of Criteria aimed at addressing Social or Ethical Concerns can be more difficult in the context of regulated public procurement procedures. Public authorities are specifically empowered to include social requirements in their conditions for the performance of contracts or to reserve certain contracts for performance by sheltered workshops or employment programmes (Articles 26 and 19 of Directive 2004/18/EC respectively).
.
My Note: DIRECTIVE 2004/18/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 31 March 2004, on the co-ordination of procedures for the award of public works contracts, public supply contracts and public service contracts.
[ For another moment, let’s just overlook the unfortunate use of disability-related language … which fails, utterly, to take account of the 2001 World Health Organization’s International Classification of Functioning, Disability & Health (ICF). See my previous Posts.]
Article 19 – Reserved Contracts
Member States may reserve the right to participate in public contract award procedures to sheltered workshops or provide for such contracts to be performed in the context of sheltered employment programmes where most of the employees concerned are handicapped persons who, by reason of the nature or the seriousness of their disabilities, cannot carry on occupations under normal conditions.
The contract notice shall make reference to this provision.
Article 26 – Conditions for Performance of Contracts
Contracting authorities may lay down special conditions relating to the performance of a contract, provided that these are compatible with Community law and are indicated in the contract notice or in the specifications. The conditions governing the performance of a contract may, in particular, concern social and environmental considerations.
ANNEX VI – Definition of Certain Technical Specifications
For the purposes of this Directive:
1. (a) ‘technical specification’, in the case of public works contracts, means the totality of the technical prescriptions contained in particular in the tender documents, defining the characteristics required of a material, product or supply, which permits a material, a product or a supply to be described in a manner such that it fulfils the use for which it is intended by the contracting authority. These characteristics shall include levels of environmental performance, design for all requirements (including accessibility for disabled persons) and conformity assessment, performance, safety or dimensions, including the procedures concerning quality assurance, terminology, symbols, testing and test methods, packaging, marking and labelling and production processes and methods. They shall also include rules relating to design and costing, the test, inspection and acceptance conditions for works and methods or techniques of construction and all other technical conditions which the contracting authority is in a position to prescribe, under general or specific regulations, in relation to the finished works and to the materials or parts which they involve ;
(b) ‘technical specification’, in the case of public supply or service contracts, means a specification in a document defining the required characteristics of a product or a service, such as quality levels, environmental performance levels, design for all requirements (including accessibility for disabled persons) and conformity assessment, performance, use of the product, safety or dimensions, including requirements relevant to the product as regards the name under which the product is sold, terminology, symbols, testing and test methods, packaging, marking and labelling, user instructions, production processes and methods and conformity assessment procedures ;
2. ‘standard’ means a technical specification approved by a recognised standardising body for repeated or continuous application, compliance with which is not compulsory and which falls into one of the following categories:
– International Standard: a standard adopted by an international standards organisation and made available to the general public ;
– European Standard: a standard adopted by a European standards organisation and made available to the general public ;
– National Standard: a standard adopted by a national standards organisation and made available to the general public.
.
In order for a Criterion … any Criterion … to be acceptable within the European Union’s Public Procurement Framework, it should be expressly linked to the subject matter of the Contract … should be specific … and should be capable of objective verification.
Beware !!
.
.
END