2013-06-08: Looking forward to some serious, collaborative and multi-disciplinary discussions on the day … and a barrel of laughs in the process (!!) …
The Informatics Research Unit for Sustainable Engineering (IRUSE) in the Department of Civil Engineering … and The Ryan Institute for Environmental, Marine and Energy Research … both at the National University of Ireland Galway (NUIG) … have jointly organized a 1-Day National Research Networking Workshop which will take place on Monday, 24 June 2013.
The NUIG ‘blurb’ for the day states … “Considering the importance of aggressive energy-efficiency measures in the Building Sector, together with the requirements for a safe, healthy, comfortable (and accessible) Built Environment … this NUIG Workshop will explore the topic of Integrated Modelling and Performance of the Built Environment.”
.
I was very pleased to receive an invitation to make a Presentation at this prestigious event …
‘Sustainable Fire Engineering Design’ – My Presentation Abstract
Fire Engineering … involves much more than mere compliance with building regulations and codes … whose fire safety objectives are limited, and whose performance requirements are sometimes inadequate and always minimal. More problematically … a fundamental conflict is mushrooming between Safe Sustainable Climate Resilient Building Design and Conventional Fire Consultancy Practice.
However … Sustainable Fire Engineering Design Solutions are:
- Reliability-based ;
- Person-centred ;
… and above all …
- Adapted to Local Context and Heritage (fr: le Patrimoine – see ICOMOS 2011) … geography, climate (incl. change, variability and severity swings), social need, culture, and economy, etc., etc.
This Presentation will discuss very rich collaborative research potential in the following areas …
- Creative Fire Engineering Concepts and Building Systems
- Fire-Induced Progressive Damage in Buildings
- Human Behaviour and Abilities in a Fire Situation
- Building Design for Firefighter Safety
- BMS – Fire Modelling – BIM
Research Output must be targeted at practical implementation in ‘real’ buildings … with actual user/construction performance carefully (i.e. reliably and precisely) monitored !
.
If anybody out there is interested in attending this NUIG Research Workshop … please contact Ms. Magdalena Hajdukiewicz (IRUSE) at: hajdukiewicz1@nuigalway.ie
.
.
POST-EVENT UPDATE: 2013-06-27 …
While it was difficult to keep the Workshop Programme, involving a series of short 10-minute presentation slots, on track … discussions during the day were engaging, energetic and extensive.
I happily look forward to a successful and collaborative outcome from the day … Multi-Disciplinary Teams producing Trans-Disciplinary Research Output … which is geared towards practical implementation in ‘real’ buildings, with actual construction and building user performance carefully (i.e. reliably and precisely) monitored !
Galway University (NUIG) Workshop Programme & Presentation Abstracts
Click the Link Above to read and/or download PDF File (193 Kb)

.
CJ Walsh Presentation: ‘Sustainable Fire Engineering Design’
Click the Link Above to read and/or download PDF File (1.78 MB)
.
However … and especially since the Workshop had been organized by IRUSE (the ‘SE’ standing for ‘Sustainable Engineering’) … it was indeed very strange to have to clarify the following points, among others:
1. The Minimum Life Cycle for a Sustainable Building is 100 Years … not 50 or 60 years !
2. Future Research Collaboration should be targeted at the multi-aspect ‘Sustainability Agenda’. The word ‘green’ (where only environmental aspects of sustainability are considered) should be actively discouraged, if not banned entirely !
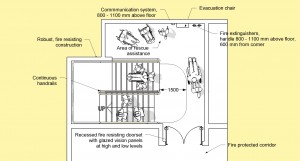
3. With regard to Good Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) … two high-level performance indicators which have been developed with the aim of protecting human health, and are both now referenced in International Standard ISO 21542: ‘Building Construction – Accessibility & Usability of the Built Environment’ … are …
– Radon Activity (incl. Rn-222, Rn-220, RnD) in a building should, on average, fall within the range of 10 Bq/m3 to 40 Bq/m3, but should at no time exceed 60 Bq/m3 ;
– Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Concentrations in a building should not significantly exceed average external levels – typically within the range of 300 parts per million (ppm) to 500 ppm – and should at no time exceed 800 ppm.
.
Galway University’s New Engineering Building
Concerning the substantive difference in meaning and scope between ‘sustainable’ and ‘green’ … there is, perhaps, no better way to illustrate this difference than to observe the atrocious ‘Accessibility-for-All’ Performance (Accessibility for People with Activity Limitations !) of the critically acclaimed (?!?) and award winning (?!?) New Engineering Building in Galway University … which flaunts its ‘über-green’ credentials …
Can you believe what’s in those photographs ?? More importantly … can you believe what’s not in those photographs ???? In such a recently completed building … “incredible” is the only answer to both questions.
.
Under International Law … lack of accessibility, or inadequate accessibility, to the social, built, virtual and economic environments … IS a denial and infringement of the basic human rights of people with activity limitations. It also limits, needlessly and unnecessarily, the numbers of potential users of those environments … which makes no sense at all.
My strong recommendation to Galway University … is to immediately commission a Competent Accessibility Consultant to give the university campus a thorough going over ! You are failing the campus user population … the local community in Galway … and Irish society generally.
My even stronger recommendation to the Architects for the New Engineering Building … RMJM Architects (Robert Matthew Johnson-Marshall) in Scotland, and Taylor Architects in Ireland … is to always commission a Competent Accessibility Consultant on all of your projects … small, medium and large … because you haven’t a bull’s notion about this important dimension of building performance !!
And remember folks … Accessibility has been clearly specified in the new International Standard ISO 21542 as including … ‘access to buildings, circulation within buildings and their use, egress from buildings in the normal course of events, and evacuation in the event of an emergency’.
.
.
END